Artificial Intelligence-based Patents: Perspectives for Practitioners and Patent Owners
A few tips to help both draft effective AI/ML-based patent applications and develop an intentional AI/ML-based patent portfolio strategy.
February 20, 2020 at 08:00 AM
6 minute read

Innovations involving artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being developed at an ever-accelerating pace. For example, Figure 1 illustrates that the number of patent applications published by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) including the phrases "artificial intelligence" and "machine learning" has increased from 373 publications in 2009 to 6,476 publications in 2019.
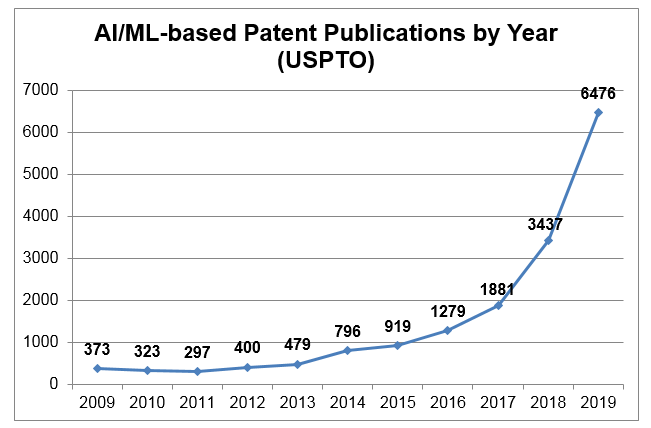
Source: Google Patents, https://patents.google.com
Practitioner Perspective: Drafting Effective AI/ML-based Patent Applications
From the outset, practitioners should gather information on the novel, non-obvious aspects of the given invention including, but not limited to:
- Input data preparation: How is data gathered, pre-processed, handled, or parsed upon use by the AI/ML model? Is the data obtained from a specific type of sensor (e.g., a camera or radar device)? What does the data represent (e.g., letters, words, Boolean values)?
- Model structure: Does the model have specific non-generic features (e.g., a neural network with non-conventional number of nodes at given layers, multiple hidden layers, etc.), and how is the input data mapped to this specific structure?
- Training phase process: How is the model trained, and in what manner (e.g., tagged input-output pairs, unsupervised learning, etc.)?
- Execution phase process: What weights are used with respect to what variables? What advantages result from execution of the AI/ML model?
- Output data post-processing / analysis: How are the outputs utilized and what do they represent (e.g., classification, recommendation, likelihoods, etc.)? Is the data used to control a specific device (e.g., a speech synthesizer or autonomous vehicle)?
- Locus of AI/ML processing: Is the substantive computing performed locally (e.g., "on the edge"), in the cloud, in multiple locations, and/or elsewhere?
- AI/ML-based hardware: Does the innovation utilize AI/ML-specific integrated circuits, such as AI/ML -optimized graphics processing units (GPUs)? How does the model structure map to such hardware?
Next, when drafting AI/ML-centric patent claims, practitioners should:
- Include a "patentable hook" in each independent claim, which hopefully relates back to the AI/ML-based nature of the invention.
- Separate training phase processes from execution phase processes by utilizing independent claim families directed to the respective methods.
- Try to incorporate as much physical structure (e.g., controller, computation unit, circuits, etc.) as possible into the claims to obviate issues with 35 U.S. § 101 (patentable subject matter). This structure can include both special hardware used for the training and execution phases, as well as physical devices that provide input data or receive output data.
- Utilize patent analytics by "testing" sample claim language to predict art unit assignments and iteratively adjust claim terms to actively avoid business method type art units (e.g., art unit 3600) or other low-allowance-rate art units.
Breaking the patent specification into multiple sections that correspond to the major elements of the AI/ML-based invention (e.g., input data preparation, model structure, training phase, etc.) can compartmentalize the disclosure and may help ensure that each novel, non-obvious detail is described thoroughly. Patent drawings should expressly illustrate each substantive claim term in a schematic-type diagram or a method flowchart.
Patent Owner Perspective: Developing an Intentional AI/ML-based Patent Portfolio Strategy
Building and maintaining an AI/ML-based patent portfolio can be expensive and time-consuming. When an invention satisfies many of the factors in the checklist below, it may indicate that preparing and filing a patent application is in line with the company's interests.
Business and Patent Portfolio Goals
First, consider the invention and how it relates to the business and patent portfolio goals of the company.
- Consider key industry players (competitors, partners, customers). Is the invention directed to technology related to key industry players? Is anyone outside of your company using the invention?
- Consider this AI/ML-based invention with respect to your own company. Is the invention directed to a fundamental/core technology and/or product of your company? Is the invention currently in use at your company?
- Consider your company's investment in this AI/ML-based invention. Has a substantial amount of money or employee hours been invested in research and development of the invention?
- Consider the impact of the AI/ML-based invention. Does the invention provide a disruptive solution to an existing problem in industry (e.g., the invention reduces power usage by 10%)?
- Consider the "shelf life" of the AI/ML-based invention. Short or long product life?
- Consider publicizing the AI/ML-based invention. Are you okay with making the invention available to public? Weigh patent rights versus trade secret protection.
- Consider patent ownership. Will the company be able to claim ownership over the patent (jointly developed)? Does the AI/ML-based code include third-party code or open-source code?
- Consider the potential market for this patent and monetization potential. Is there potential for licensing revenue or sale of the patent (and return license)? Is there interest in enforcing the patent?
- Consider copying and reverse-engineering of the invention. Is the invention difficult to reverse-engineer (e.g., an AI/ML-based application running on a private cloud server)?
- Consider international market/competitors. Should you protect the invention in foreign jurisdictions?
Patent Law Considerations
Second, consider the AI/ML-based invention and whether legal requirements to obtain a patent can be satisfied.
- Consider the prior art. Is the invention substantially different than conventional systems (e.g., neural network with novel structure or novel input data mapping)?
- Consider potential claim scope in light of the prior art. Would possible claim scope be too narrow and hard to enforce or easy for a competitor to design around?
- Consider enforcement of patent rights. Is it easy for you to identify when someone is using the invention?
- Consider patent eligibility. Is the invention "directed to" laws of nature, mathematical theories, etc.? An algorithm (e.g., a neural network) in and of itself is not patentable subject matter, but an algorithm utilized in a specific method or system could represent patentable subject matter.
- Consider whether the invention is sufficiently developed. Is the invention past "idea" stage (e.g., AI/ML-based code has been developed and maybe implemented in tests, training phase completed)? When test results exist, consider whether to include them in a patent application.
Aaron Gin, Ph.D. is a partner with McDonnell Boehnen Hulbert & Berghoff LLP. Dr. Gin has broad experience in preparing and prosecuting U.S. and foreign applications for patents and trademarks. He provides advice in support of patent validity, infringement, patentability analyses, and litigation matters in the electrical and computing technology areas.
Michael S. Borella is a partner with McDonnell Boehnen Hulbert & Berghoff LLP and serves as a Co-Chair of the firm's Software & Business Methods Practice Group. Dr. Borella provides legal and technological advice in support of validity, infringement, patentability analyses, and litigation matters.
Joseph A. Herndon is a partner with McDonnell Boehnen Hulbert & Berghoff LLP and serves as a Co-Chair of the firm's Software & Business Methods Practice Group. Mr. Herndon's prosecution experience includes all phases of U.S. and foreign patent and trademark prosecution, client counseling, due diligence, and opinion work regarding validity, infringement, and enforceability of patents.
This content has been archived. It is available through our partners, LexisNexis® and Bloomberg Law.
To view this content, please continue to their sites.
Not a Lexis Subscriber?
Subscribe Now
Not a Bloomberg Law Subscriber?
Subscribe Now
NOT FOR REPRINT
© 2025 ALM Global, LLC, All Rights Reserved. Request academic re-use from www.copyright.com. All other uses, submit a request to [email protected]. For more information visit Asset & Logo Licensing.
You Might Like
View AllLaw Firms Mentioned
Trending Stories
- 1Relaxing Penalties on Discovery Noncompliance Allows Criminal Cases to Get Decided on Merit
- 2Reviewing Judge Merchan's Unconditional Discharge
- 3With New Civil Jury Selection Rule, Litigants Should Carefully Weigh Waiver Risks
- 4Young Lawyers Become Old(er) Lawyers
- 5Caught In the In Between: A Legal Roadmap for the Sandwich Generation
Who Got The Work
J. Brugh Lower of Gibbons has entered an appearance for industrial equipment supplier Devco Corporation in a pending trademark infringement lawsuit. The suit, accusing the defendant of selling knock-off Graco products, was filed Dec. 18 in New Jersey District Court by Rivkin Radler on behalf of Graco Inc. and Graco Minnesota. The case, assigned to U.S. District Judge Zahid N. Quraishi, is 3:24-cv-11294, Graco Inc. et al v. Devco Corporation.
Who Got The Work
Rebecca Maller-Stein and Kent A. Yalowitz of Arnold & Porter Kaye Scholer have entered their appearances for Hanaco Venture Capital and its executives, Lior Prosor and David Frankel, in a pending securities lawsuit. The action, filed on Dec. 24 in New York Southern District Court by Zell, Aron & Co. on behalf of Goldeneye Advisors, accuses the defendants of negligently and fraudulently managing the plaintiff's $1 million investment. The case, assigned to U.S. District Judge Vernon S. Broderick, is 1:24-cv-09918, Goldeneye Advisors, LLC v. Hanaco Venture Capital, Ltd. et al.
Who Got The Work
Attorneys from A&O Shearman has stepped in as defense counsel for Toronto-Dominion Bank and other defendants in a pending securities class action. The suit, filed Dec. 11 in New York Southern District Court by Bleichmar Fonti & Auld, accuses the defendants of concealing the bank's 'pervasive' deficiencies in regards to its compliance with the Bank Secrecy Act and the quality of its anti-money laundering controls. The case, assigned to U.S. District Judge Arun Subramanian, is 1:24-cv-09445, Gonzalez v. The Toronto-Dominion Bank et al.
Who Got The Work
Crown Castle International, a Pennsylvania company providing shared communications infrastructure, has turned to Luke D. Wolf of Gordon Rees Scully Mansukhani to fend off a pending breach-of-contract lawsuit. The court action, filed Nov. 25 in Michigan Eastern District Court by Hooper Hathaway PC on behalf of The Town Residences LLC, accuses Crown Castle of failing to transfer approximately $30,000 in utility payments from T-Mobile in breach of a roof-top lease and assignment agreement. The case, assigned to U.S. District Judge Susan K. Declercq, is 2:24-cv-13131, The Town Residences LLC v. T-Mobile US, Inc. et al.
Who Got The Work
Wilfred P. Coronato and Daniel M. Schwartz of McCarter & English have stepped in as defense counsel to Electrolux Home Products Inc. in a pending product liability lawsuit. The court action, filed Nov. 26 in New York Eastern District Court by Poulos Lopiccolo PC and Nagel Rice LLP on behalf of David Stern, alleges that the defendant's refrigerators’ drawers and shelving repeatedly break and fall apart within months after purchase. The case, assigned to U.S. District Judge Joan M. Azrack, is 2:24-cv-08204, Stern v. Electrolux Home Products, Inc.
Featured Firms
Law Offices of Gary Martin Hays & Associates, P.C.
(470) 294-1674
Law Offices of Mark E. Salomone
(857) 444-6468
Smith & Hassler
(713) 739-1250






